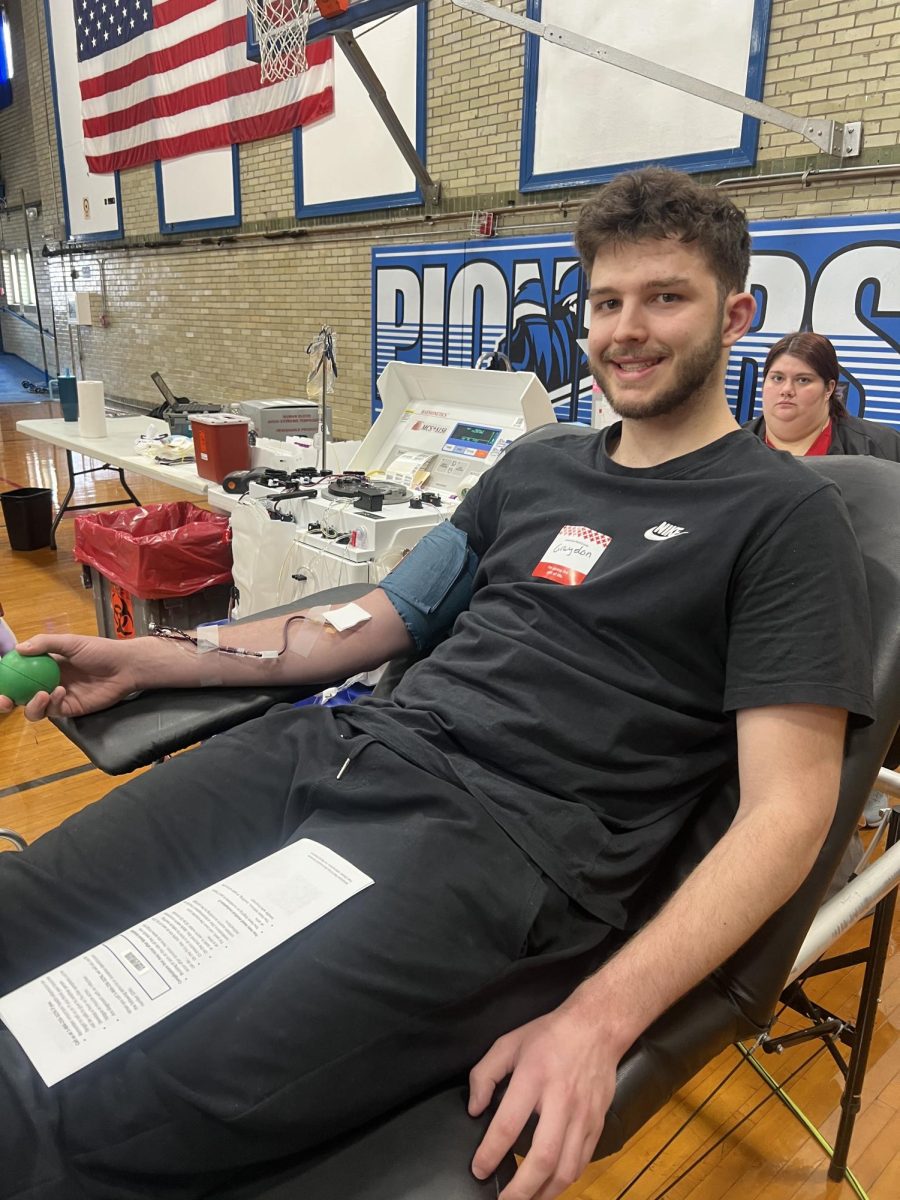
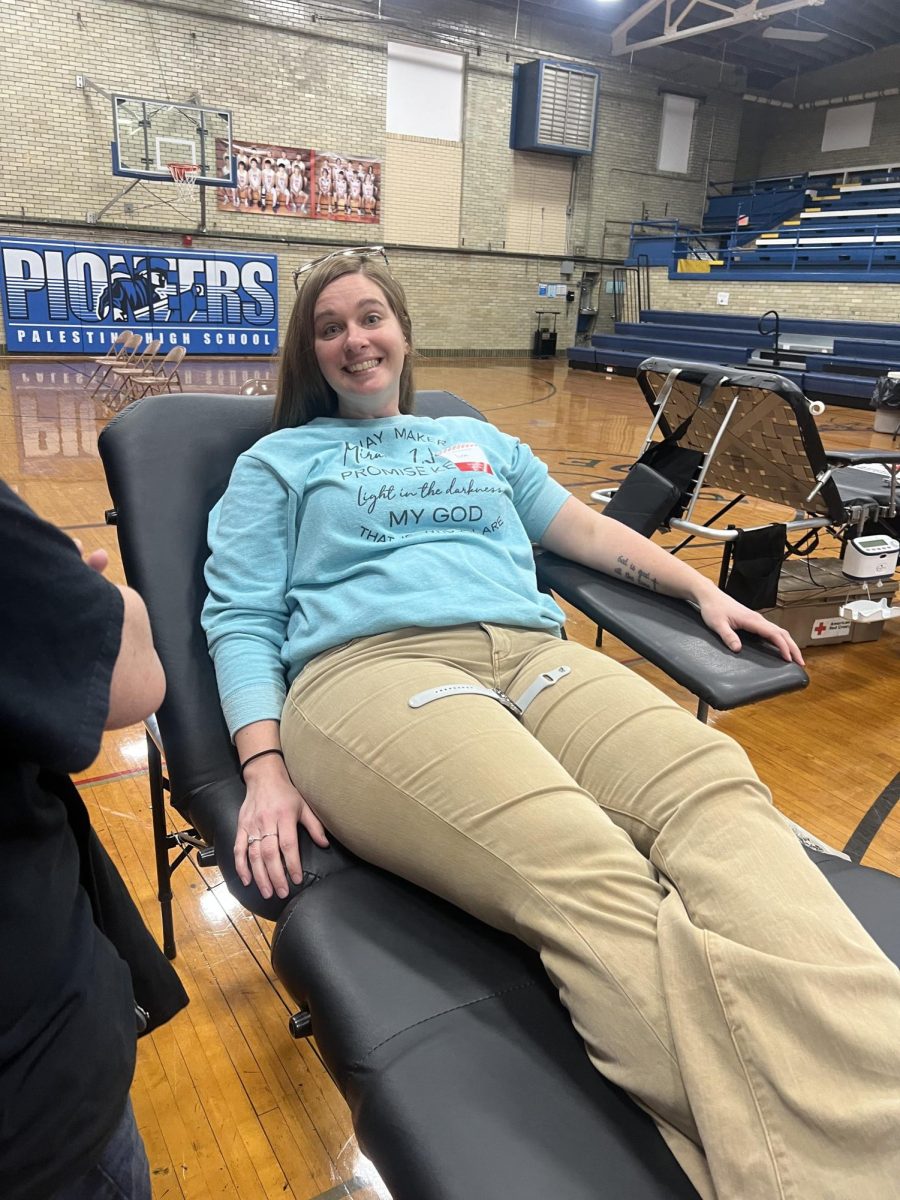
Although donating blood is a great thing that saves many peoples´ lives, it can also be dangerous. Athletes that want to donate blood should not participate in any straining activities after giving. There are many side effects that could impair their abilities. Some risks of donating blood are reduced oxygen-carrying capacity, iron deficiency, and recovery time.
Reduced Oxygen-Carrying Capacity: Donating blood reduces the volume of red blood cells, which are responsible for carrying oxygen to the muscles. This can lead to lessening the athlete’s endurance and/or overall performance.
Iron Deficiency: Donating blood can also deplete iron stores, which are crucial for red blood cell production and oxygen transport. Athletes that donate are far more likely to have iron deficiency. This can make them tired, light headed, or even short of breath.
Recovery Time: After donating blood, your body can take up to several weeks to replenish the red blood cells and iron because of what was lost.
It is recommended that athletes avoid donating blood while they are in their sport to avoid health issues. If it is necessary to donate, make sure to be very well hydrated and eat nutritious meals to help the recovery process go faster. The athletes should also be in communication with their coaches, athletic trainer, and maybe even a doctor to make sure it is safe for them to donate blood.